Home > Information > press release > NCC Establishes Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced
Therapeutics (C-CAT) to Aggregate and Manage Information on
Cancer Genomic Medicine and Promote Its Use
NCC Establishes Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced
Therapeutics (C-CAT) to Aggregate and Manage Information on
Cancer Genomic Medicine and Promote Its Use
June 1, 2018
National Cancer Center
in Japanese
On June 1, the National Cancer Center (President: Hitoshi Nakagama, Location: Chuo-ku, Tokyo, Japan) will establish the Center for Cancer Genomics and Advanced Therapeutics (“C-CAT,” Director: Hiroyuki Mano) as a new hub for cancer genomic medicine—one of the focal points in the third phase of the Basic Plan to Promote Cancer Control Programs, which the Japanese government is executing under the Cancer Control Act. C-CAT will aggregate and manage nationwide information on genomic medicine and implement a system for appropriate use of this information to develop new types of medicine.
Background
With regard to genomic medicine in Japan, in 2017 the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare convened a Roundtable Consortium on the Promotion of Cancer Genomic Medicine. In addition to providing Japanese citizens with early access to the world’s leading-edge cancer genomic medicines, the consortium called for the capitalization on Japan’s strengths to develop innovative treatment methods, contribution to other Asian countries by integrating the nation’s knowledge of, and creation of a framework to lead cancer genomic medicine on a global scale. Furthermore, the consortium clarified ownership of the constructed framework as an asset of Japanese citizens and set directions for the functions and roles of medical institutions providing cancer genomic medicine, and institutions that aggregate, manage and promote the use of cancer genomic medicine (Report, June 27, 2017).
To build up a system incorporating the new introduction to healthcare in phases, in February 2018 the Japanese government designated 11 hospitals throughout Japan to serve as core hospitals for cancer genomic medicine. The government also appointed 100 facilities as liaison hospitals to work with the core hospitals and set fiscal 2019 as the year to provide cancer genomic medicine under the national health insurance system.
Following these government policies, the National Cancer Center will coordinate an integrated network of core hospitals for cancer genomic medicine and cancer genomic medicine liaison hospitals throughout Japan (hereinafter, “Core Hospitals, etc.”). To aggregate, and deploy cancer genomic medicine information to advance the quality of healthcare offered under health insurance, and to devise new modalities of healthcare, C-CAT is established with national government funds.
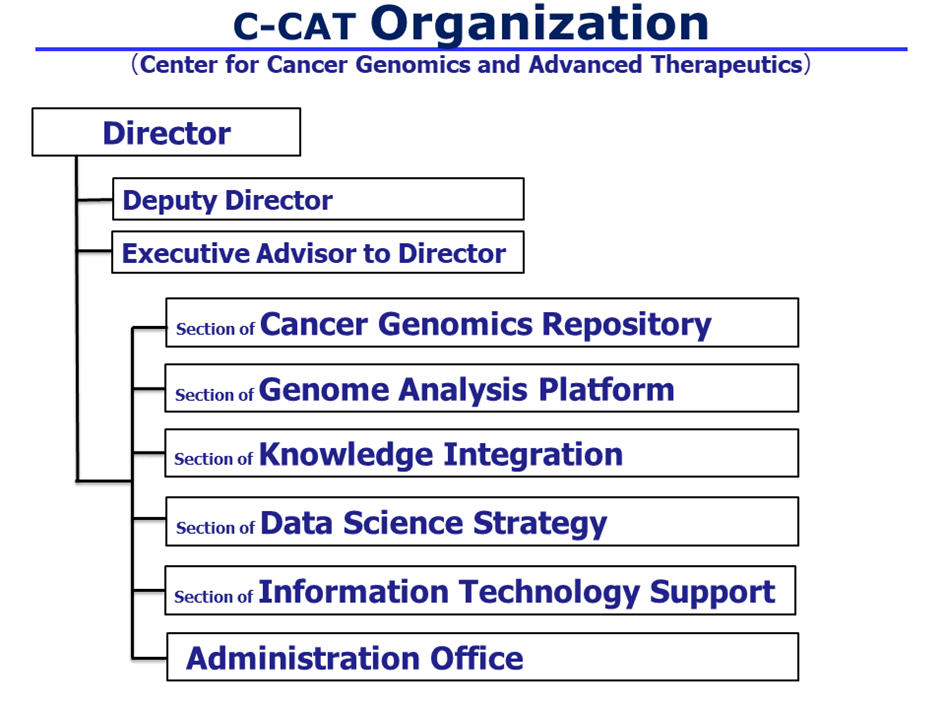
Roles of C-CAT
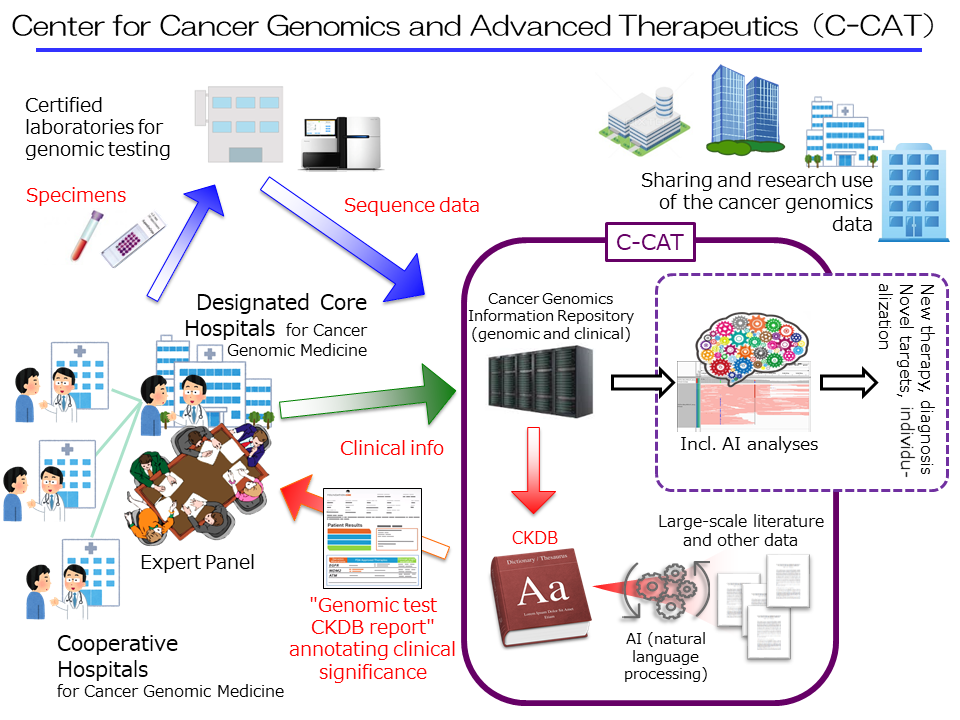
First, the center will develop and create a “cancer genomics information repository*1,” a master database for cancer genomic medicine and research that is scheduled to commence trial operations in early 2019. The center will also construct a Cancer Knowledge DataBase (CKDB), for cancer genomic medicine. The center will fully utilize this framework and promote cancer genomic medicine in Japan alongside the Core Hospitals, etc.
- Control quality and advance genomic diagnosis of cancer
- The center will secure Japanese clinical and genomic information at domestic public institutions, create a CKDB optimized for Japan, contribute to decision making by expert panels*2 at core hospitals for cancer genomic medicine.
- The center will communicate information on cancer genomic medicine with the Japanese public, and advocate policies underpinned by data accumulated nationwide.
- Lead data sharing
- Promote data sharing among Core hospitals, etc. following appropriate protocol, and promote cancer care covered by national healthcare insurance.
- Promote clinical trials, research and development
- Provide a robust foundation for clinical studies and investigator-initiated clinical trials utilizing core data.
- Serve as resource for drug development, and for personalized medicine, also opening avenues to private corporations.
- Conduct research, and nurture talent in preparation for the introduction of whole genome sequencing to healthcare
About the Cancer Genome Information Repository*1
In addition to genomic information on cancer patients from Core Hospitals, etc., C-CAT will aggregate and manage clinical information (through data templates and electronic data capture (EDC) systems), including information on therapeutic drug efficacy and adverse events. At the same time, C-CAT will build a system for quality control with Core Hospitals, etc., with avenues for corrections when required. The center will analyze mutations from the genetic information received from each patient, referencing against the CKDB to create a “CKDB report on cancer genome testing,” which is to be provided to core hospitals for cancer genomic medicine.
The center will also serve as a gateway to share part of the clinical and genomic information accumulated, to advance the quality of healthcare covered by national healthcare insurance, and promote clinical studies at Core Hospitals, etc. The center will also provide datasets for secondary use, for medicine research and development by academia and the private sector. Additionally, the center aims to establish a system supporting Core Hospitals, etc as necessary.
About Expert Panels*2
Cancer genomic medicine is supported by the analyses of genomic information of cancer cells of individual patients, providing underpinning data to facilitate the attending physician’s selection of an optimal treatment method for individual patients. This process, for extracting medically useful information from the source data for a comprehensive genomic analysis, calls for deliberations by multiple specialists. This body is called an “expert panel.” Expert panels are set at all core hospitals for cancer genomic medicine, and the reports these panels produce are sent back to the attending physicians. C-CAT will be providing core hospitals for cancer genomic medicine with a “CKDB report on cancer genome testing” as material among others for deliberation by expert panels.
References (Japanese Only)
Basic Plan to Promote Cancer Control Programs (Phase 3) <Resolved by the Cabinet, March 9, 2018) >http://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/0000183313.html
Report by the Expert Meeting for Cancer Genomic Medicine Promotion Consortium
http://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi2/0000169238.html
First Investigative Committee Related to the Designation of Core Hospitals for Cancer Genomic Medicine (Documents)
http://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/shingi2/0000194192.html
Media inquiries
National Cancer Center
Office of Public Relations, Strategic Planning Bureau
5-1-1 Tsukiji, Chuo-ku, Tokyo 104-0045, Japan
Telephone:+81-3-3542-2511
FAX:+81-3-3542-2545
E-mail: ncc-admin●ncc.go.jp(●replace to @)
