Home > Information > Launch of an Asian international collaborative prospective study on 6 advanced cancers common in Asia
Launch of an Asian international collaborative prospective study on 6 advanced cancers common in AsiaEstablishment of a database of genomic analysis and clinical information by liquid biopsy, for developing personalized treatment
December 23, 2021
National Cancer Center Japan
in Japanese
- An international collaborative prospective study on 6 advanced cancers, which occur frequently in Asia, will be launched to build and analyze a database of blood-based genomic profiles and clinical information.
- The project involves five companies and eight Asian countries including Japan. We are to build a database for research and development in Asia, using cancer gene panel tests appropriate for each cancer, while ensuring compliance with all applicable privacy laws.
- Through analysis of the database, we aim to identify genomic abnormalities that can be used as therapeutic targets, and to develop personalized treatments for advanced cancers common in Asia.
Summary
The National Cancer Center Hospital Japan will launch an international joint research project (Asian multicenter prospective study of circulating TumoR DNA SequencINg; A-TRAIN) in eight Asian countries (Japan, Korea, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Taiwan, Thailand and Vietnam) to develop novel treatments based on genomic abnormalities for cancers common in Asia. For patients with cervical cancer, ovarian cancer, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, endometrial cancer and breast cancer, the database will be constructed and analyzed by examining genomic abnormalities comprehensively by liquid biopsy, together with clinical information such as treatment details and prognosis.
As these cancers occur more frequently in Asia and are more difficult to treat, there is a strong need to develop new treatments. It is difficult to anticipate that the pharmaceutical developers of Europe and the United States would take the lead in research and development addressing these cancers, therefore, it is necessary to drive research and development through collaboration in the Asian region. In this study, we aim to solve these problems by using blood for genetic analysis. Genomic analysis of blood samples is expected to be used more widely in clinical practice as it is a less invasive procedure, enables testing and analysis according to the course of treatment, and facilitates quality control of samples. This study will be conducted as an international collaborative study under the "Asian clinical TriaLs network for cAncerS (ATLAS) project" which aims to accelerate the implementation of clinical research and trials and early drug development in the Asian region.
A-TRAIN; Asian multicenter prospective study of circulating TumoR DNA SequencINg
A-TRAIN is an Asian multicenter prospective study*1 that comprehensively analyzes genomic abnormalities in the blood of cancer patients with metastatic and/or recurrent diseases. In this study, cancer-related genes will be analyzed using a genomic panel test for blood, and information on genomic abnormalities in each cancer will be analyzed with patient information. This study will be done in collaboration with companies and the National Cancer Center Research Institute Japan.(Figure 1)
We will comprehensively analyze circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA)*2 in the blood of approximately 500 patients with six cancer types who have metastatic and/or recurrent disease, and at the same time collect clinical information to build and analyze a database, with the aim of identifying genetic abnormalities that may be therapeutic targets, and conducting clinical trials.
Figure 1. Overview of A-TRAIN
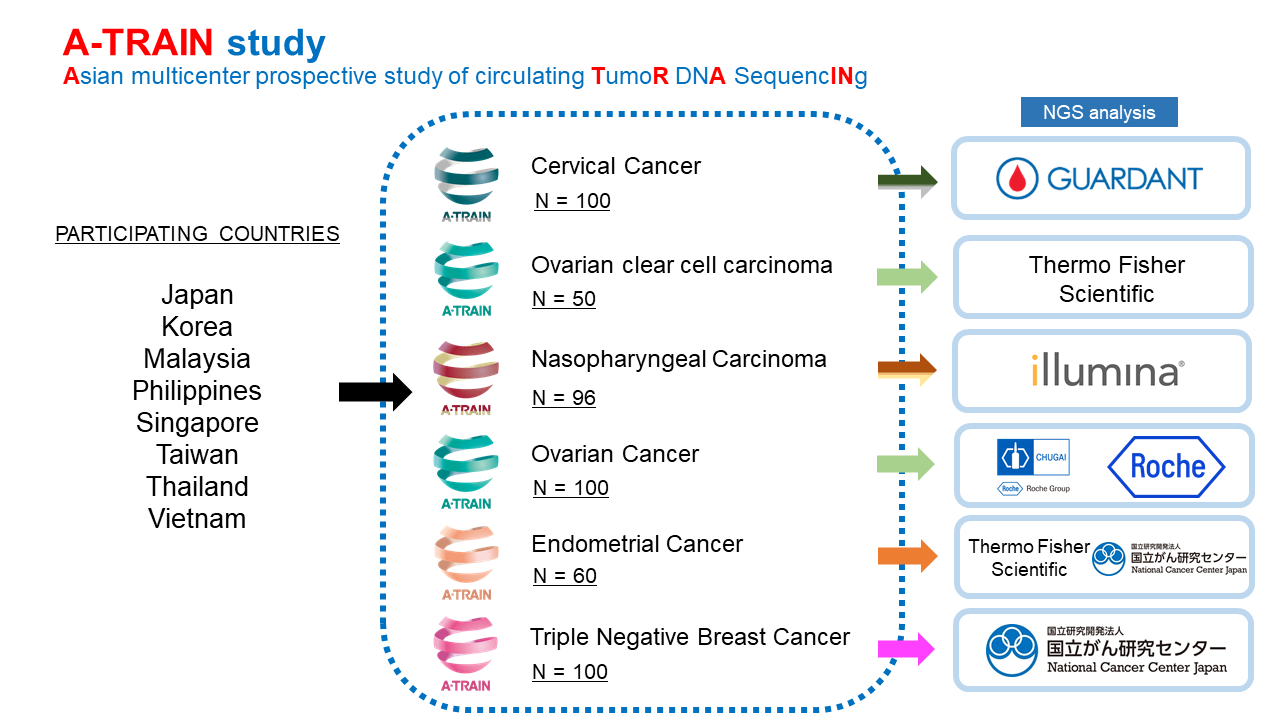
Cervical Cancer cohort
Start date
December 2021
Participating countries
Japan, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, Vietnam
Number of registrants
100
Genetic analysis
Guardant Health Asia, Middle East & Africa (AMEA)
Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma cohort
Start date
December 2021
Participating countries
Japan, Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, Vietnam
Number of registrants
50
Genetic analysis
Thermo Fisher Scientific Japan Group (hereafter referred to as “Thermo Fisher”)
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma cohort
Start date
December 2021
Participating countries
Japan, Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Singapore, Taiwan, Vietnam
Number of registrants
96
Genetic analysis
Illumina, Inc.
Ovarian Cancer cohort
Start date
December 2021
Participating countries
Japan, Taiwan, Vietnam
Number of registrants
100
Genetic analysis
Chugai Pharmaceutical Co Ltd and Roche Ltd
Endometrial Cancer cohort
Start date
February 2022
Participating countries
Japan, Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Taiwan, Vietnam
Number of registrants
60
Genetic analysis
Thermo Fisher and National Cancer Center Research Institute, Japan
Triple-negative Breast Cancer cohort
Start date
January 2022
Participating countries
Japan, Korea, Philippines, Thailand, Singapore, Vietnam
Number of registrants
100
Genetic analysis
National Cancer Center Research Institute, Japan
Participating institutions (as of 23 December 2021)
- National Cancer Center Hospital
- St. Luke’s Medical Center, Philippines
- Hospital Umum Sarawak, Malaysia
- University Malaya Medicine Center, Malaysia
- Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- National Cancer Institute, Malaysia
- National University Cancer Institute, Singapore
- National Taiwan University Hospital, Taiwan
- National Cancer Hospital of Vietnam, Vietnam
- Ho Chi Minh City Oncology Hospital Vietnam
Participating companies
- Guardant Health Asia, Middle East & Africa (AMEA)
- Thermo Fisher
- Illumina Corporation
- Chugai Pharmaceutical Co.
- Roche Corporation
- Intellim Corporation
- SRL
- Eurofins
Message from the Principal Investigator

Kan Yonemori
The National Cancer Center Hospital has started the Asian multicenter prospective study of circulating TumoR DNA SequencINg (A-TRAIN) after discussions with doctors and researchers in Asia to promote the development of Asian therapies for Asian cancer patients.
A-TRAIN, a train going through Asia.
What do you think of when you hear the word "TRAIN"?
Possibly a steam locomotive moving powerfully forward, a train taking you on an exciting adventure in life, stopping by stations where you meet people and say goodbye.
This project started its journey as A-TRAIN with the support of the National Cancer Center Hospital, Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development, various companies, and the enthusiasm, passion and energy of those involved as the driving force. We will continue to advance with each of us playing own roles, as we welcome in others.
Let's hold hands and drive our aspirations into the dream train of ideas that will take us to an exciting future in Asia.
Background
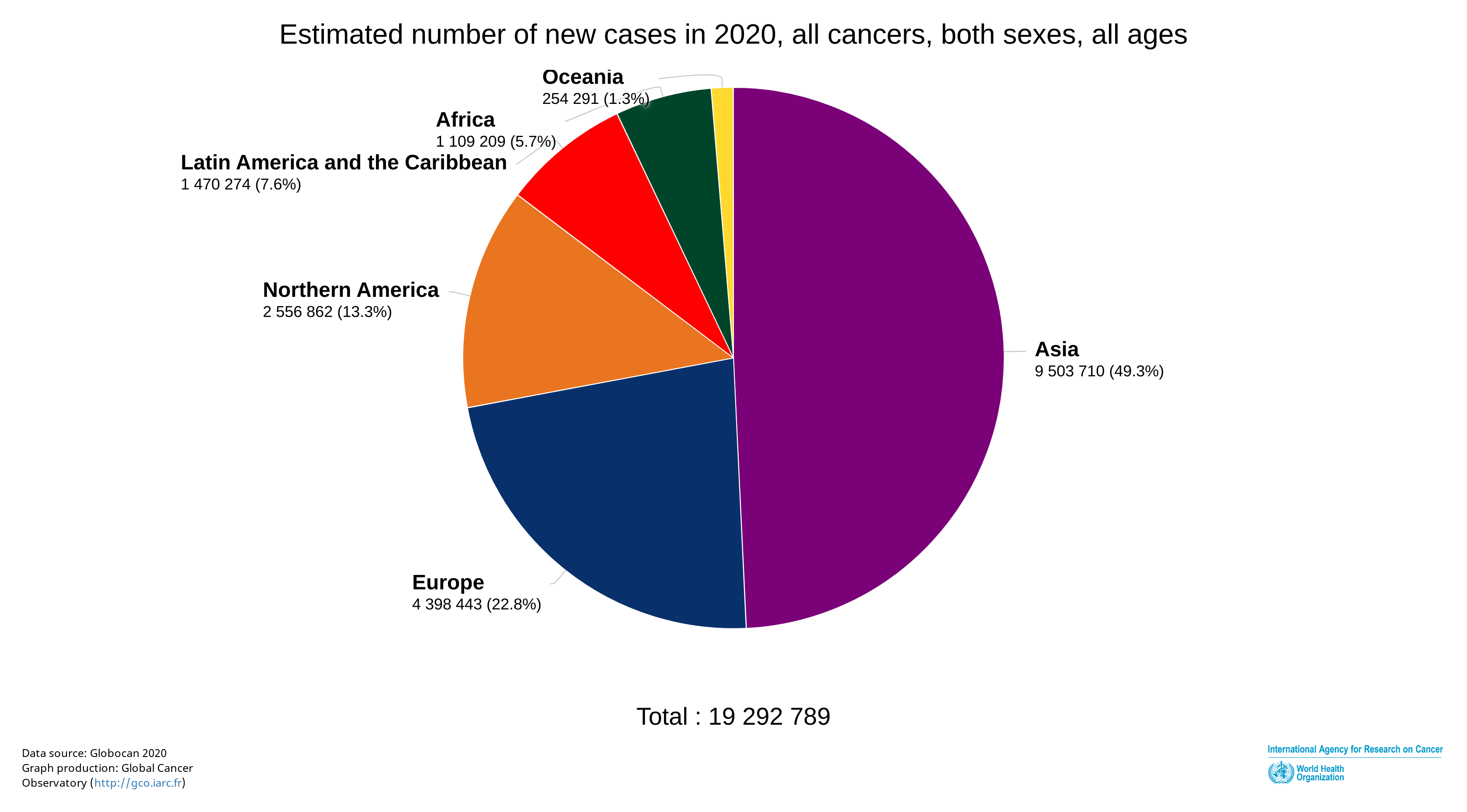
According to statistics in 2020, the number of newly diagnosed cancers worldwide is estimated at 19.3 million, and of deaths resulting from cancer at 9.96 million. Of these new cancer cases, Asia accounts for about half (Figure 2).
In developing countries, including Asian nations, cancer types unique in Asia, such as cervical cancer, pharyngeal cancer, and liver cancer, in addition to the extension in life expectancy, the high smoking rate, and the lack of cancer screening schemes are believed to be behind this phenomenon.
Figure 2. Estimated number of newly diagnosed cancer cases worldwide(2020)
In recent years, genomic testing for cancer has been advanced by the development of cancer gene panel tests*3 that determine treatments based on the genomic profiles of cancers. The OncoGuideTM NCC OncoPanel System, developed by the National Cancer Center Japan, was approved in Japan as a medical device on December 25, 2018. However, this test cannot be performed on patients with cervical cancer, pharyngeal cancer, etc., from whom sufficient tumor tissue cannot be collected. Therefore, developing a gene panel test using blood samples called liquid biopsy is necessary. Genomic analysis using blood samples is attracting attention for its low invasiveness, its ability to provide real-time information on genetic abnormalities, and its use for monitoring after treatment completion.
ATLAS Project
The "ATLAS project: Asian clinical TriaLs network for cAncerS project" is a Japan-led initiative to establish a platform for international collaborative trials with Malaysia, Thailand, the Philippines, Indonesia and Vietnam, which are actively promoting cancer treatment development in the Asian region. We aim to develop early-stage drug development for cancer in the Asian region through the introduction of cancer genomic medicine and the implementation of investigator-initiated clinical trials and corporate trials for regulatory approval. It also aims to improve drug access in Asia and to promote the full-scale introduction of cancer genomic medicine in the region, thereby enhancing development capabilities in Asia as a whole and solving Asia's specific problems on its own.
Conducting clinical trials in collaboration with other Asian countries is expected to speed up completion of the trials and lead to accelerated approval of new drugs for us all. Finally, we aim to build a well-established clinical trial network in the Asian region, to lead the world in therapeutic development.
September 9, 2020 Press Release
https://www.ncc.go.jp/jp/information/pr_release/2020/0909/index.html
Research Funds
This project is funded by ‘Kobayashi Foundation, Principal Investigator: Dr Kan Yonemori, Chief, Department of Medical Oncology, National Cancer Center Hospital, and “Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), Principal Investigator: Dr. Kazuaki Shimada, Hospital Director, National Cancer Center Hospital”
Terminology
*1Prospective study
Prospective studies start in the present and continue collecting new data and samples forward in time, with the cooperation of patients. Retrospective studies, on the other hand, is a study that investigates various subjects using medical records, clinical specimens, and other information recorded in medical records, test result data, and tissue samples.
*2Circulating tumor DNA
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) are produced when tumors shed small pieces of their genetic material into the bloodstream. These traces of this tumor DNA can be detected in the blood using digital sequencing technology. In the future, the technology is expected to be widely used for various purposes in cancer treatment such as companion diagnostics to determine therapeutic agents, screening, monitoring of treatment efficacy, and evaluation of residual disease after curative treatments such as surgery or radiotherapy.
*3 Cancer gene panel tests
A cancer gene panel test examines a large number of genes simultaneously in a single test using an analyzer called a "next-generation sequencer," which reads a large amount of genomic information at high speed using cancer tissues taken from biopsies or surgeries. If a gene mutation is found with a drug expected to be effective against it, we will consider using that drug, including clinical trials. The National Cancer Center has developed a genetic testing system (OncoGuide™ NCC OncoPanel System) using multiplex gene panel test reagents that can detect mutations, amplifications, and fusions of cancer-related genes in a single assay, in collaboration with Sysmex Corporation, for rapid and accurate identification of genetic variants. The product has been approved for manufacturing and marketing as an in vitro diagnostic drug and medical device (December 25, 2018) and for insurance coverage (June 2019) for "patients with solid tumors for which no standard treatment is available or for which standard treatment has been terminated due to local progression or metastasis”.
Cancer Gene Panel Test OncoGuideTM NCC Oncopanel System added to Health Insurance Coverage list
https://www.ncc.go.jp/en/information/press_release/20190717/20190717152024.html
Enquiries
On Research
International Trial Management Section, Clinical Research Support Office
National Cancer Center Hospital, Japan
E-mail:NCCH1905_office●ml.res.ncc.go.jp
Office of Public Relations
Strategic Planning Bureau
National Cancer Center Japan
TEL: +81-3-3542-2511
E-mail:ncc-admin●ncc.go.jp


