Annual Report 2017
Central Radioisotope Division
Masamichi Ishiai, Yutaka Yamada, Gen Fujii, Junko Suzuki
Introduction
The Central Radioisotope Division is a joint usage facility, composed of the Research Support Core of the Fundamental Innovative Oncology Core (FIOC) of the National Cancer Center (NCC) Research Institute. We provide advanced technical training and education for researchers in the NCC.
Our team and what we do
Our division manages radioisotope (RI) materials, gamma-ray irradiator (Gammacell 220 with Co-60 source, and Gammacell 440 Ex with Cs-137 source), and radiation related equipment. The important roles of our division are exposure control of radiation workers and management of the radiation control area.
The facility utilizing information
In 2017, both the number of gamma irradiation (Table 1) and used amount of RI (Table 2) were decreased, possibly because of the temporal unavailability of our division caused by relocation of the Research Institute.
Table 1. Number of use of the gamma-ray irradiator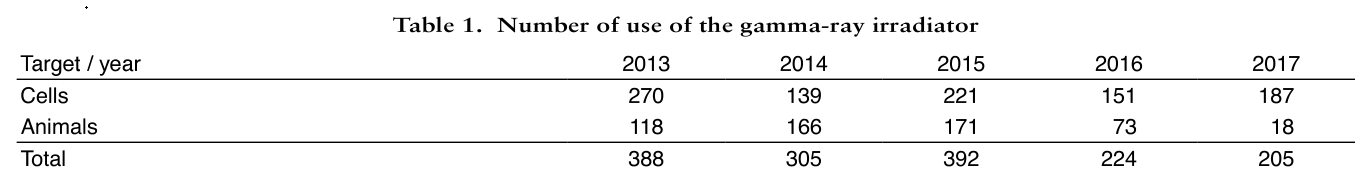

Future prospects
Recently, live imaging technology for cells and/or animals has been developing, and the usage of radionuclide for molecular imaging such as positron emission tomography (PET) has been increased. In the NCC, boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) has been started, and this caused the increased opportunities of handling neutron-irradiated cells in our division. In addition, basic and/or clinical research intended to radionuclide therapy would be started. The management, equipment, and education responsible for these new-age radiation technologies for cancer research will urgently be needed in our division.
List of papers published in January 2017 - March 2018
Journal
1. Knies K, Inano S, Ramirez MJ, Ishiai M, Surralles J, Takata M, Schindler D. Biallelic mutations in the ubiquitin ligase RFWD3 cause Fanconi anemia. J Clin Invest, 127:3013-3027, 2017
2. Onuma W, Asai D, Tomono S, Miyamoto S, Fujii G, Hamoya T, Nagano A, Takahashi S, Masumori S, Miyoshi N, Wakabayashi K, Mutoh M. Anticarcinogenic Effects of Dried Citrus Peel in Colon Carcinogenesis Due to Inhibition of Oxidative Stress. Nutr Cancer, 69:855-861, 2017
3. Miyamoto S, Komiya M, Fujii G, Hamoya T, Nakanishi R, Fujimoto K, Tamura S, Kurokawa Y, Takahashi M, Ijichi T, Mutoh M. Preventive Effects of Heat-Killed Enterococcus faecalis Strain EC-12 on Mouse Intestinal Tumor Development. Int J Mol Sci, 18:2017
4. Noma N, Fujii G, Miyamoto S, Komiya M, Nakanishi R, Shimura M, Tanuma SI, Mutoh M. Impact of Acetazolamide, a Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor, on the Development of Intestinal Polyps in Min Mice. Int J Mol Sci, 18:0, 2017
5. Mochizuki AL, Katanaya A, Hayashi E, Hosokawa M, Moribe E, Motegi A, Ishiai M, Takata M, Kondoh G, Watanabe H, Nakatsuji N, Chuma S. PARI Regulates Stalled Replication Fork Processing To Maintain Genome Stability upon Replication Stress in Mice. Mol Cell Biol, 37:2017
6. Kadoda K, Moriwaki T, Tsuda M, Sasanuma H, Ishiai M, Takata M, Ide H, Masunaga SI, Takeda S, Tano K. Selective cytotoxicity of the anti-diabetic drug, metformin, in glucose-deprived chicken DT40 cells. PLoS One, 12:e0185141, 2017
7. Ishiai M, Sato K, Tomida J, Kitao H, Kurumizaka H, Takata M. Activation of the FA pathway mediated by phosphorylation and ubiquitination. Mutat Res, 803-805:89-95, 2017
8. Inano S, Sato K, Katsuki Y, Kobayashi W, Tanaka H, Nakajima K, Nakada S, Miyoshi H, Knies K, Takaori-Kondo A, Schindler D, Ishiai M, Kurumizaka H, Takata M. RFWD3-Mediated Ubiquitination Promotes Timely Removal of Both RPA and RAD51 from DNA Damage Sites to Facilitate Homologous Recombination. Mol Cell, 66:622-634.e8, 2017
9. Hamoya T, Miyamoto S, Tomono S, Fujii G, Nakanishi R, Komiya M, Tamura S, Fujimoto K, Toshima J, Wakabayashi K, Mutoh M. Chemopreventive effects of a low-side-effect antibiotic drug, erythromycin, on mouse intestinal tumors. Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition, 60:199-207, 2017
