Annual Report 2020
Central Radioisotope Division
Masamichi Ishiai, Gen Fujii, Hiroshi Tanooka, Kaima Tsukada, Rikiya Imamura, Hideyuki Watanuma
Introduction
The Central Radioisotope Division is a joint usage facility composed of the Research Support Core of the Fundamental Innovate Oncology Core (FIOC) of the National Cancer Center (NCC) Research Institute. We provide advanced technical training and education for researchers in the NCC. We also support and advice on radiation biological research.
The Team and What We Do
Our division manages radioisotope (RI) materials, gamma-ray irradiators (Gammacell 220 with Co-60 source and Gammacell 40 Exactor with Cs-137 source), and radiation-related equipment to promote advanced cancer research in a smooth manner. Our division also develops radiation management studies so that researchers can use RI resources safely and effectively.
Research activities
We have focused on the study of molecular mechanisms of cellular responses such as DNA damage responses, DNA repair, and apoptosis pathways after DNA damage, including irradiation. We have also investigated the molecular mechanism of chemical carcinogenesis and /or cancer chemoprevention. The research topics were presented at international and/or domestic academic conferences and published as treatise.
The facility utilization information
The usage frequency of gamma-ray irradiator and the used amount of RI for the past five years are shown in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. While the frequency of radiation-related experiments decreased in the relocation period of the Research Institute (2017), they have been steadily recovered.
Table 1. Number of uses for gamma-ray irradiator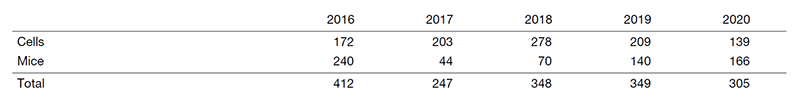

Table 2. Used amounts of radioisotopes (MBq)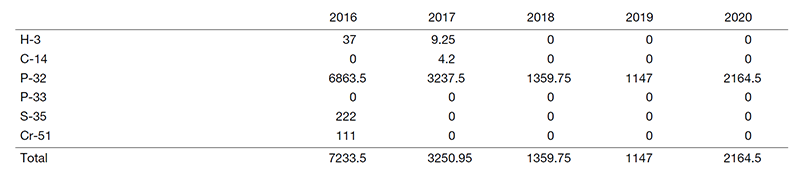

Education
We provide an annual course for education and training in radiation biology, handling of RI, and operation of gamma-ray irradiators. Two graduate school students are trained in our division.
Future Prospects
In recent years, live imaging technology of cells and/or animals has been developing, and the usage of radionuclides for molecular imaging such as positron emission tomography (PET) has increased. A clinical trial for cancer patients using the boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) has initiated, which has increased the opportunities to handle neutron-irradiated cells in our division. Moreover, it is intended to start basic and/or clinical research on radionuclide therapy. The management, equipment, and education required for these new-age radiation technologies for cancer research will be urgently needed in our division.
List of papers published in 2020
Journal
1. Tsukada K, Shimada M, Imamura R, Saikawa K, Ishiai M, Matsumoto Y. The FHA domain of PNKP is essential for its recruitment to DNA damage sites and maintenance of genome stability. Mutat Res, 822:111727, 2021
2. Hamoya T, Fujii G, Iizumi Y, Narita T, Komiya M, Matsuzawa Y, Miki K, Kondo T, Kishimoto S, Watanabe K, Wakabayashi K, Sakai T, Toshima J, Mutoh M. Artesunate inhibits intestinal tumorigenesis through inhibiting wnt signaling. Carcinogenesis, 42:148-158, 2021
3. Tanooka H, Inoue A, Takahashi RU, Tatsumi K, Fujikawa K, Nagao T, Ishiai M, Chiwaki F, Aoyagi K, Sasaki H, Ochiya T. Bacterial SOS Genes mucAB/umuDC Promote Mouse Tumors by Activating Oncogenes Nedd9/Aurkb via a miR-145 Sponge. Mol Cancer Res, 18:1271-1277, 2020
4. Matsui M, Sakasai R, Abe M, Kimura Y, Kajita S, Torii W, Katsuki Y, Ishiai M, Iwabuchi K, Takata M, Nishi R. USP42 enhances homologous recombination repair by promoting R-loop resolution with a DNA-RNA helicase DHX9. Oncogenesis, 9:60, 2020
5. Kurokawa Y, Fujii G, Tomono S, Miyamoto S, Hamoya T, Takahashi M, Narita T, Komiya M, Kobayashi M, Higami Y, Mutoh M. The Radical Scavenger NZ-419 Suppresses Intestinal Polyp Development in Apc-Mutant Mice. J Clin Med, 9:2020
6. Mutoh M, Yoshimura K, Fujii G, Nakamura T, Takeshita T, Wakabayashi K, Sakai T, Ishikawa H. Very Long-Term Treatment with a Lactobacillus Probiotic Preparation, Lactobacillus casei Strain Shirota, Suppresses Weight Loss in the Elderly. Nutrients, 12:2020
7. Adachi S, Hamoya T, Fujii G, Narita T, Komiya M, Miyamoto S, Kurokawa Y, Takahashi M, Takayama T, Ishikawa H, Tashiro K, Mutoh M. Theracurmin inhibits intestinal polyp development in Apc-mutant mice by inhibiting inflammation-related factors. Cancer Sci, 111:1367-1374, 2020
