Annual Report 2023
Section of Knowledge Integration
Shinji Kohsaka, Katsuyuki Ikarashi, Kayoko Tao, Megumi Ikeda, Taro Shibata, Yasushi Goto, Kazuya Tsuchihara
Introduction
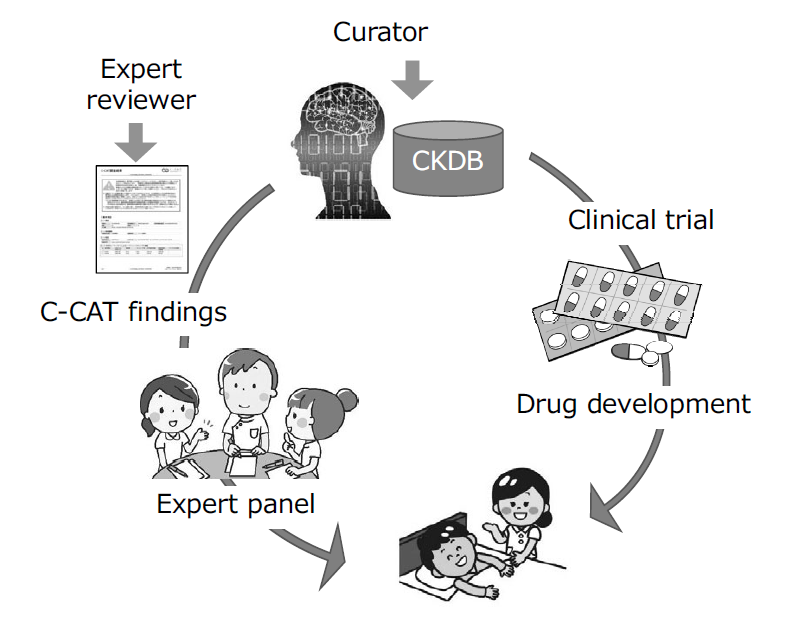
The Section of Knowledge Integration is constructing the Cancer Knowledge Database (CKDB) to control the quality and advance the genomic diagnosis of cancer. The section coordinates with the information repository system developed by the Section of Cancer Genomics Repository and optimizes the CKDB for Japan to support the expert panels at core hospitals for cancer genomic medicine.
The Team and What We Do
- Development of Cancer Knowledge Database
The CKDB was developed and maintained to improve the quality of cancer genome testing. A curator team consisting of 25 clinical oncologists and bioinformaticians was organized to maintain the system, updating data from clinical trials, medicines and marker evidence monthly.
- Providing the C-CAT findings
We have provided expert panel C-CAT findings, a report summary of clinical trials, medicines and marker evidence to annotate clinical significance of variants found by cancer panel testing performed by clinical laboratories. We have also established and maintained a management system to control the quality of C-CAT findings by standardizing the review process by expert reviewers, who are equivalent to M.D. or Ph.D. level.
Research Activities
The CKDB was developed by collecting, standardizing and integrating the information of marker evidence, anti-cancer therapies and clinical trials. Using the CKDB, we constructed a system to generate C-CAT findings. We also developed the CKDB-portal to search, query and curate the knowledge stored in CKDB. As of March 2024, information on 696 clinical trials, 1,652 medicines, and 191,179 items of marker evidence are stored in CKDB. We signed non-disclosure agreements with four pharmaceutical companies to receive detailed information from171clinical trials between April 2023 and March 2024. A total of 21,536 C-CAT findings were provided to expert panels of core hospitals between April 2023 and March 2024.
Future Prospects
C-CAT findings support the expert panel with information on the newest evidence, anti-cancer therapies and clinical trials. As a result, genome medicine will be uniformly and efficiently promoted. Furthermore, the promotion of clinical trials will activate new drug development in Japan, leading to the discovery of evidence and contributing significantly to progress in cancer medicine (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Development of CKDB to improve the quality of genome medicine