Home > Organization > Division of Functional Imaging(Kashiwa) > Research Summary > Preclinical and in vivo imaging studies
Preclinical and in vivo imaging studies
We are investigating preclinical and in vivo imaging tests towards clinical application of new molecular probes and imaging techniques.
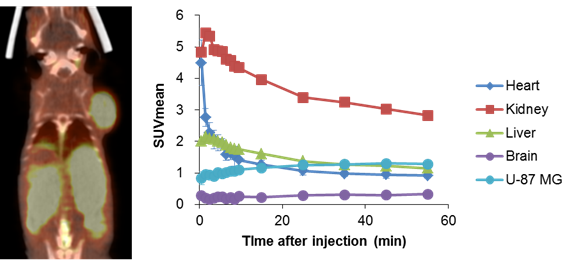
Evaluation of usefulness of FBPA PET/CT tests in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) (Collaboration with the Department of Diagnostic Radiology at Central Hospital)
Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), in which thermal neutron beam is irradiated to tumor cells containing boronic compounds, is expected to be a new therapeutic strategy for intractable tumors. Sufficient uptake of boronic compounds in tumor cells is a key to the success of this treatment. We have experimentally demonstrated that PET tests with FBPA, a 18F-labeled compound of boronophenylalanine, would be useful to estimate the uptake of boronic compounds in the tumors and to predict the effects of BNCT.
Prediction of chemosensitivity of DDS drugs by using SPECT tests (Collaboration with Eisai Co., Ltd.)
Since drug delivery system (DDS) can enhance therapeutic effects of anti-cancer agents and reduce their adverse effects, anti-cancer DDS agents are actively investigated. But, DDS agents are not always effective. We estimated the uptake of liposomal agents by evaluating the accumulation of radionuclide-encapsulated liposomes in the tumors by using SPECT/CT tests and successfully predicted the therapeutic effects of these drugs based on the results obtained from SPECT/CT images. Tumors with good accumulation of radioactive liposomes often showed significant enhancement of therapeutic effects by using liposomal drugs.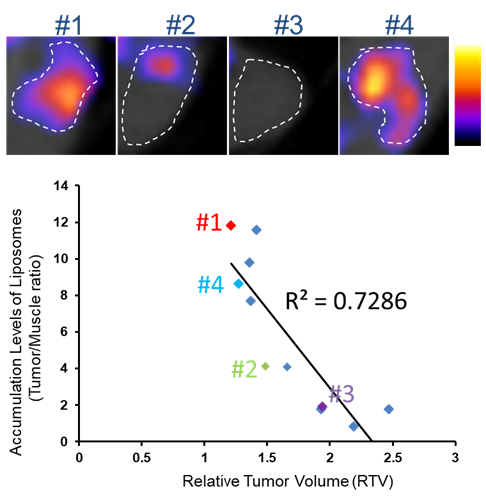
- Reprinted from Cancer Science, vol 107, Ito K, Hamamichi S, et al., Radiolabeled liposome imaging determines an indication for liposomal anticancer agent in ovarian cancer mouse xenograft models. Cancer Sci 60-67, Copyright (2016), with permission from Wiley Publishing.
- Ito K, Hamamichi S, Asano M, Hori Y, Matsui J, Iwata M, Funahashi Y, Umeda IO, Fujii H: Radiolabeled liposome imaging determines an indication for liposomal anticancer agent in ovarian cancer mouse xenograft models. Cancer Sci 107(1): 60-67, 2016
Optimization of radiation therapy for hepatic cancer by MRI with superparamagnetic iron oxide (SPIO) contrast agents
Application of radiation therapy to hepatic malignancies has been extended due to the advance in irradiation technology such as intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and proton beam therapy. However, the preciseness of irradiation to hepatic tumors can be affected by respiratory movement and the monitoring of irradiated areas in the liver is clinically important. We proposed a method to visualize irradiated areas inside the liver using SPIO contrast media that show delayed washout in the irradiated liver tissues. The feasibility of this method was validated by animal experiments.
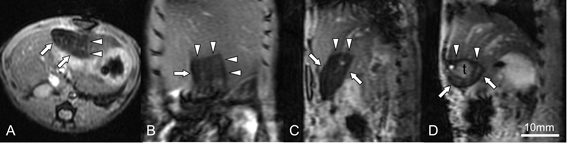
- Reprinted from Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, vol 45, Furuta T, Yamaguchi M, et al., Persistent T2*-hypointensity of the liver parenchyma after irradiation to the SPIO-accumulated liver: An imaging marker for responses to radiotherapy in hepatic malignancies. J Magn Reson Imaging 303-312, Copyright (2016), with permission from International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- Furuta T, Yamaguchi M, Minami M, Ohtomo K, Fujii H: Persistent T2*-hypointensity of the liver parenchyma after irradiation to the SPIO-accumulated liver: An imaging marker for responses to radiotherapy in hepatic malignancies. J Magn Reson Imaging 45(1): 303-312, 2017.
