Home > Organization > Division of Translational Informatics(Kashiwa)
Division of Translational Informatics(Kashiwa)
News
Introduction
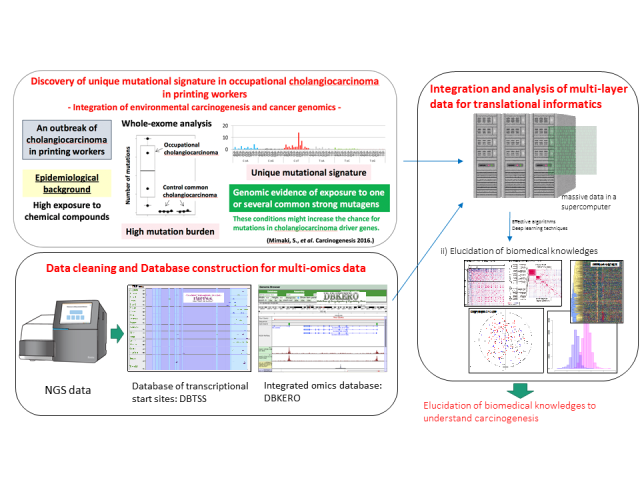
It is necessary to obtain high-quality clinical information in clinical trials for cancer research. Besides, multi-omics data such as genome, transcriptome, etc. from patient specimens, animal and cell model samples are indispensable to investigate the carcinogenesis mechanism and the effects of drugs. The relationship between microbiome present in humans and cancer is also one of the hot topics. Several new multi-omics techniques have been developed in recent years, and many researchers are producing high-quality data such as clinical sequence and/or single cell omics data. To verify the hypotheses obtained from these data, we are using a carcinogenesis model system such as organoids, which are 3D culture systems of cancer cells.
On the other hand, the amount of data generated from these omics techniques has increased day by day. Not only medical and biological knowledge but also bioinformatics which extract meaningful information effectively is essential to integrate and analyze those data. Currently, we are designing an efficient pipeline for data processing and constructing web database servers for user convenience. Our lab, translational informatics, is trying to aim for discoveries to overcome cancer by maximizing the valuable clinical multi-omics data accumulated in the National Cancer Center.
Discovery of new knowledge by integration analysis using medical and biological big data. Medicine and biology enter the era of big data. A massive amount of data is produced daily from various instruments such as sequencers, and the data are registered into the public database. However, these data are not fully utilized, unfortunately. Many tools for dry analysis are available; however, there is no meaning unless we can extract useful knowledge from the data. Furthermore, it is still a challenging task to integrate different types of data for discovering new knowledge. A supercomputer is very helpful to detect comprehensive correlations among multi-omics data such as genome (DNA), transcriptome (RNA), metabolome (metabolite), metagenome (microorganism). We are trying to extract new medical and biological knowledge based on such data and bioinformatics techniques.