MASTER KEY プロジェクト > プロジェクトについて > MASTER KEY Project Overview
MASTER KEY Project Overview
MASTER KEY Project Overview
MASTER KEY Project
Why rare cancer?
- Delayed treatment development
- Difficult to conduct a randomized trial due to limited number of patients
- Industries are rarely interested in such a small market
- Molecular background is not well investigated
- Few hospitals with sufficient function for precise diagnosis and treatment
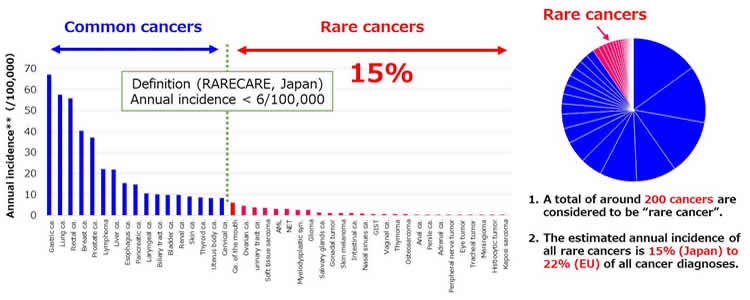
- Rare cancer is not so rare
- The annual incidence of all rare cancer occupies 15% of all cancer diagnosis in Japan
Rare Cancer Center in NCC (since 2014)

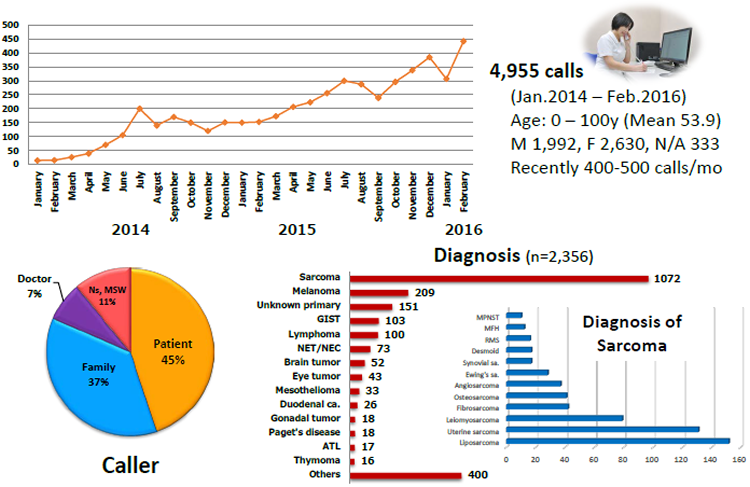
NCC Rare Cancer Hotline
MASTER KEY Project
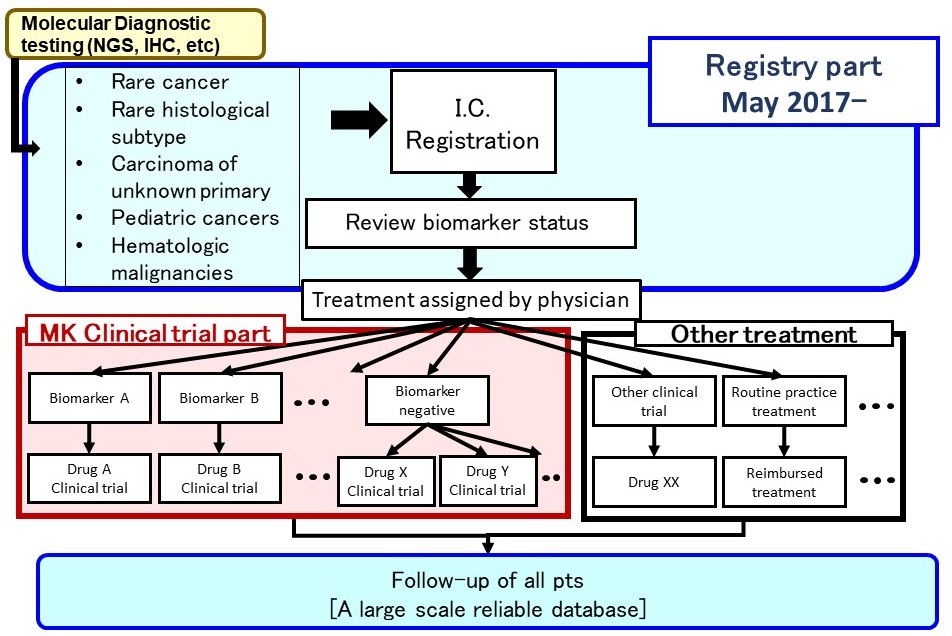
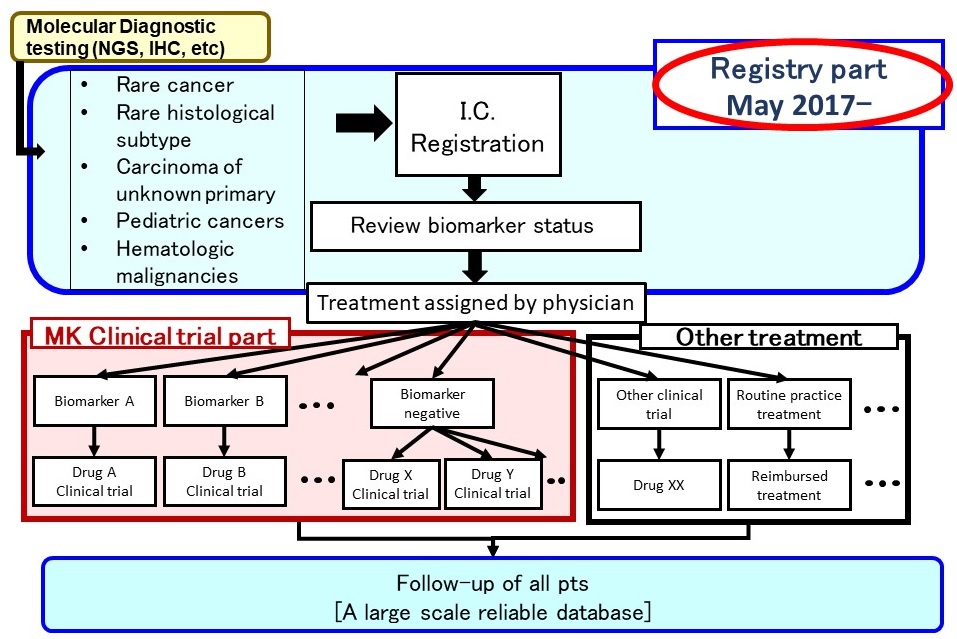
Registry part
- Aim
- Comprehensive database for rare cancer
Molecular background, natural history, treatment outcomes, etc - Use the data for applications for regulatory approval
Reliable historical control data - Assignment to clinical trials
-Biomarker-targeted and non-biomarker-targeted clinical trials
-If no clinical trial is available patients will receive treatment options outside of clinical trials
- Comprehensive database for rare cancer
- Collaboration with industries
- Joint project with 13 industries
- Funding, study drugs
- Industry-sponsored sub-study
- Joint project with 13 industries
- Accrual target
- >= 800patients/year
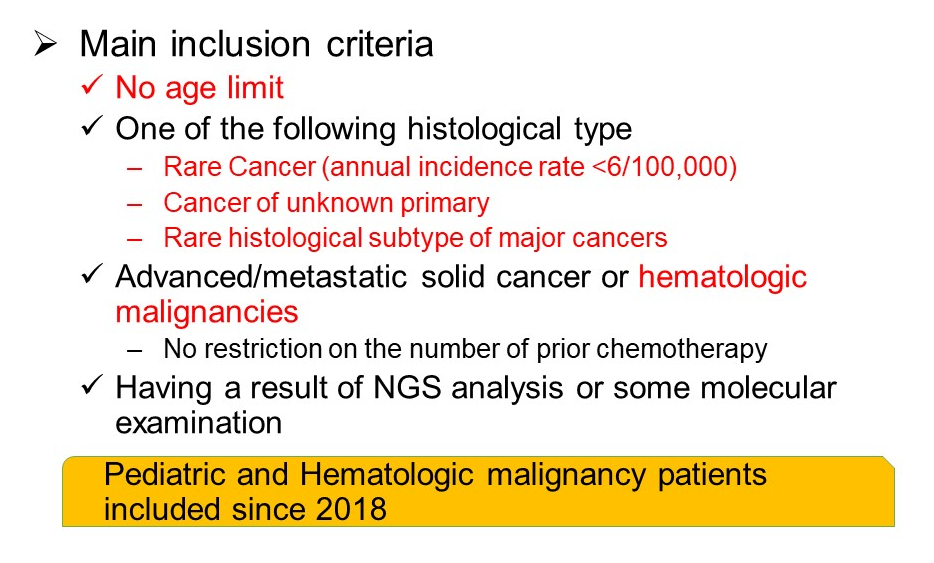
Registry part: Eligibility Criteria
Main inclusion criteria
Registry Part: Progress
Opened in May 2017
- Expected accrual rate: 800patients per year
- Study period:16 years and more (continuous development)
Progress as of July 2025
- Accrual: more than 5000 patients
- Interim study reports: every six months
MASTER KEY Project
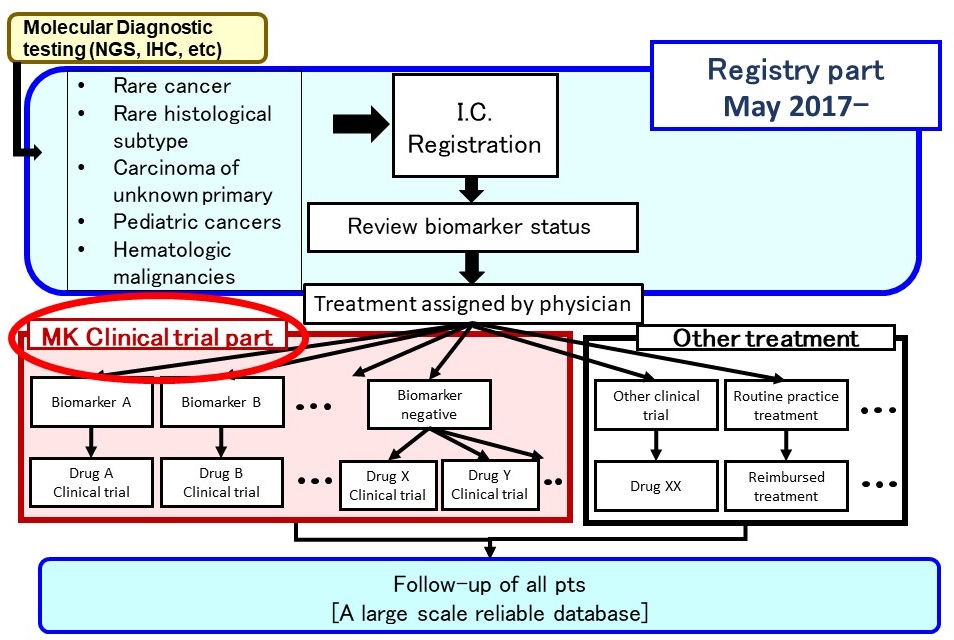
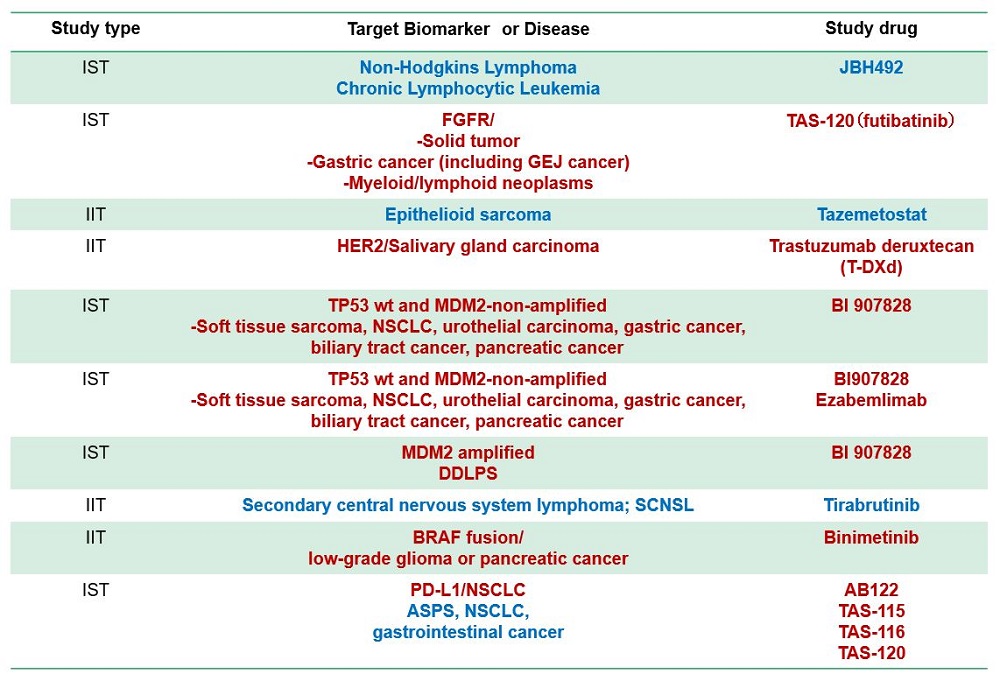
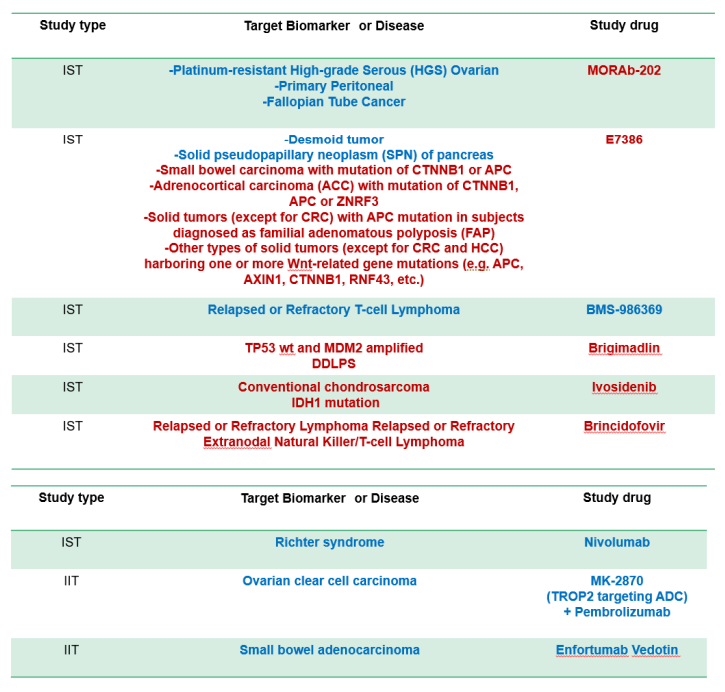
Sub-study (Clinical trial part)
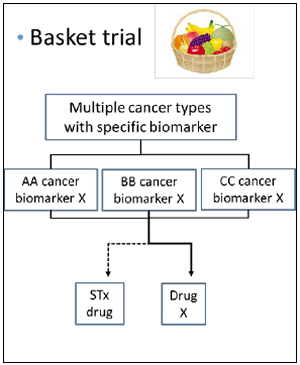
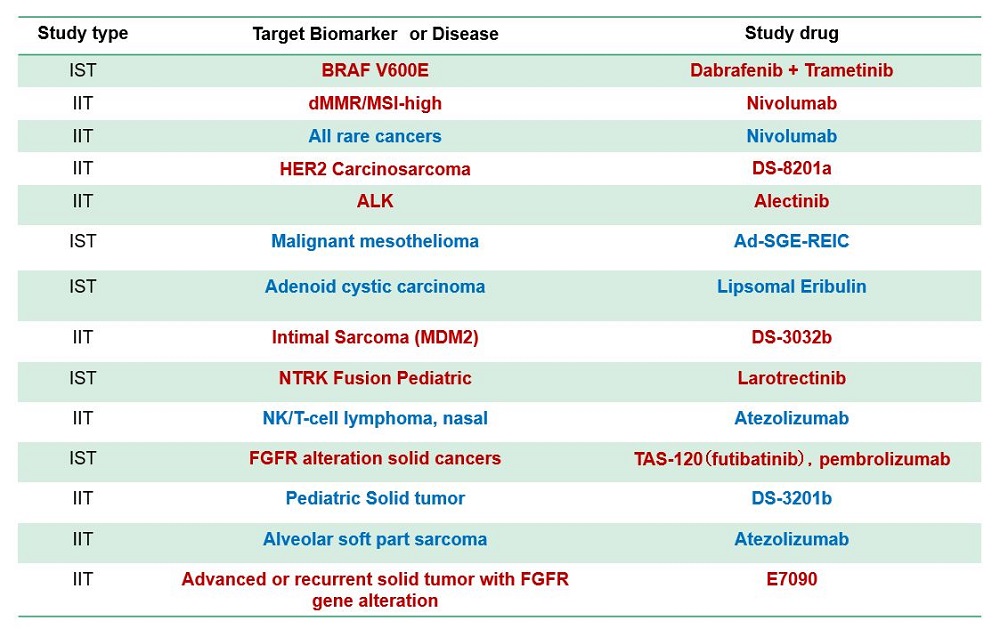
- Several sub-studies are conducted as a basket trial
- Marker(+): BRAF-V600, ALK, MDM2, HER2 etc.
- Marker(-): Immune checkpoint inhibitors, etc
- Aim
- to expand drug indication to rare cancer Typical sub-study design
- Single-arm phase 2
- Primary endpoint, response rate
- 15-25 patients with bayesiandesign
Sub-study

Collaboration between industries and academia
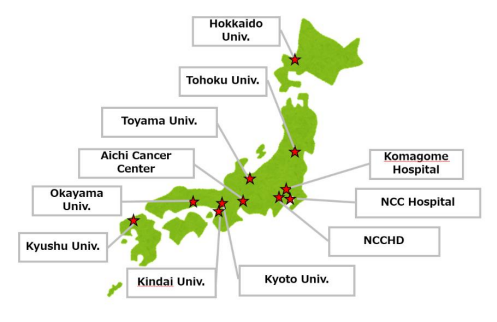
Collaborating institutions
- National Cancer Center Hospital
- Kyoto University Hospital (Joined August 2018)
- Hokkaido University Hospital (Joined April 2019)
- Kyushu University Hospital (Joined April 2019)
- Tohoku University Hospital (Joined February 2020)
- National Center for Child Health and Development (Joined February November 2021)
- Aichi Cancer Center (Joined May 2022)
- Tokyo Metropolitan Cancer and Infectious Diseases Center Komagome Hospital (Joined April 2024)
- Toyama University Hospital (Joined May 2024)
- Okayama University Hospital (Joined September 2024)
- Kindai University Hospital (Joined October 2024)
Collaborating industries

Collaboration with 13 industries

Advantages for academia
- Obtain stable funding from industries for the registry
- Obtain investigational drug/funding for investigator-initiated sub-studies
- Propose industry-sponsored sub-studies for the registered patients
Advantages for industries
- Obtain interim study reports periodically
- Request detailed analysis of the registry data
- Utilize the registry data as a reliable historical control for industry-sponsored trials
- Accelerate the patient accrual for the industry-sponsored sub-studies
Summary: MASTER KEY Project
MASTER KEY Registry
- Collaboration with 13 industries and 11 institutions
- Started since May 2017
- More than 800 patients/year
- Accrual: more than 5000 patients
MASTER KEY Sub-study
- 36 trials are being conducted
- Collaboration with industries